“A VERTIPORT
is an area of land, water, or structure used or intended to be used forthe landing and take-off of VTOL aircraft.“
Easa (European Union Aviation Safety Agency)
So vertiports are dedicated areas that provide the necessary infrastructure for the safe commercial air transport of passengers or cargo traveling VTOL.
Urban air mobility requires vertiports which must be:
– easily accessible;
– with good connection services to roads, railway stations, buses, etc.
Vertiports can be found:
– at street level;
– on top of buildings.
Vertiport can be: vertihub, vertiport, vertistop.
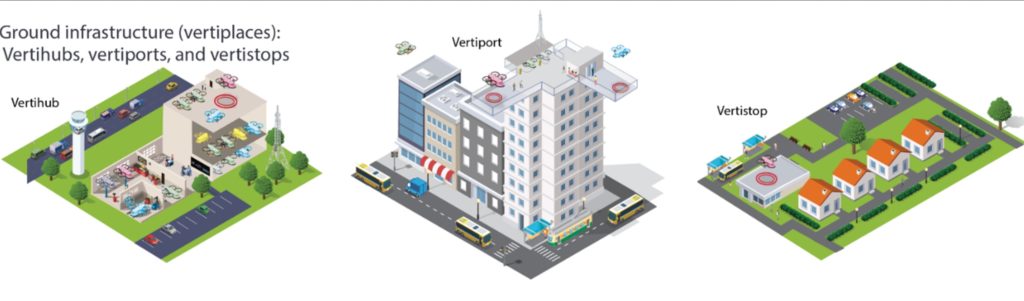
Vertihubs Vertihubs are the largest category facility and will likely exist on the periphery of urban areas due to the large physical footprint and demands on the power grid and other physical infrastructure. Vertihubs will have enough space to store aircraft overnight when not in use as well as serve as multimodal hubs connecting passengers to public transport and private vehicles.
Vertihubs are the largest category facility and will likely exist on the periphery of urban areas due to the large physical footprint and demands on the power grid and other physical infrastructure. Vertihubs will have enough space to store aircraft overnight when not in use as well as serve as multimodal hubs connecting passengers to public transport and private vehicles.
Vertihubs will also have significant maintenance, repair, and overhaul capabilities to allow aircraft to undergo more intensive maintenance than other vertiplaces.
Vertihubs may also provide passenger facilities similar to an airport, such as retail facilities and passenger screening facilities, if necessary. (Source: Nasa)
Vertiports Vertiports will be placed in heart of urban cores and serve as major sites for both passenger and cargo boarding and disembarkation.
Vertiports will be placed in heart of urban cores and serve as major sites for both passenger and cargo boarding and disembarkation.
Compared to vertihubs, vertiports will lack heavy MRO facilities but will likely have a basic maintenance staff.
Vertiports will have multiple pads, but likely one or two primary TLOF areas.
Energy infrastructure needs will be significant, but not as demanding as vertihubs and be limited to quick charging and battery swapping. Basic customer waiting areas similar to those that heliports have today are likely to exist as well as some basic security screening. (Source: Nasa)
Vertistops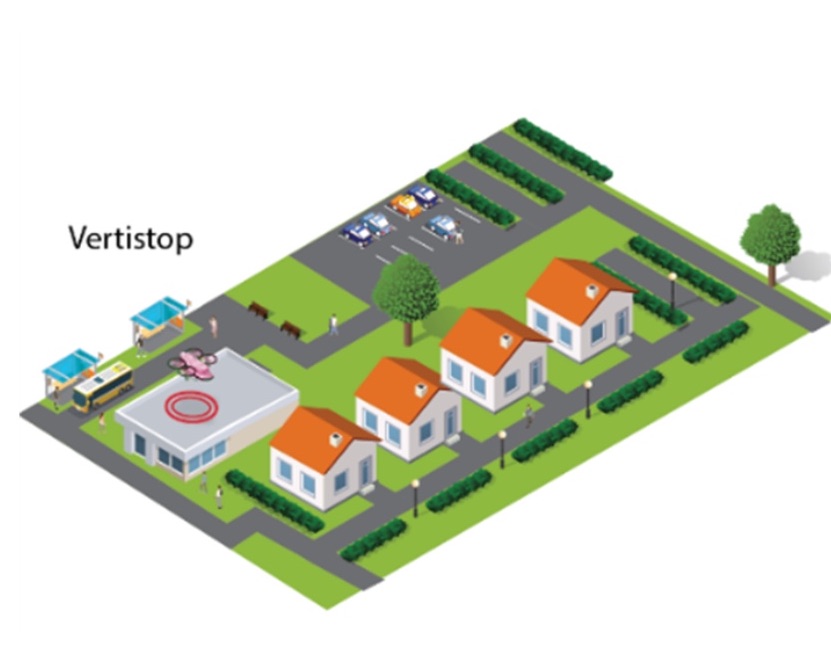 Vertistops will be the smallest element of the vertiport network and contain one TLOF area with one or two pads. Vertistops have the lowest physical footprint and serve as a connection point to the vertiplace network for suburban areas.
Vertistops will be the smallest element of the vertiport network and contain one TLOF area with one or two pads. Vertistops have the lowest physical footprint and serve as a connection point to the vertiplace network for suburban areas.
Vertistops will also serve asm multimodal connection points, but only to a handful of transport modes and will serve primarily to connect passengers with automobiles, buses, and other mobility options for transportation to deliver them the last mile. MRO (Maintenance, Repair and Operations) facilities will likely be scant to nonexistent and basic passenger holding areas and weather monitoring systems will exist to enable flights. (Source: Nasa)